The Structure of Top-Performing Webmail Systems
Email plays a significant role in our everyday routines, and it’s decisive to be aware of secure service providers. On average, people dedicate more than five hours daily to managing their work and personal emails. However, it needs more robust security despite its convenience and efficiency, especially when utilizing popular platforms such as Gmail or Outlook.
This is one of the most vulnerable entry points for hackers to compromise your organization’s sensitive data. To safeguard your correspondence and the valuable information exchanged daily, opting for a secure service provider becomes imperative.
Web app testing includes manual, automated, and exploratory testing, each with advantages and disadvantages. Choosing the best approach depends on the project’s requirements and complexity. Web app testing should be treated as a vital software development aspect.
Webmail Systems
Top-performing webmail systems, like Gmail, Outlook.com, and Yahoo Mail, have evolved over the years to provide users with a seamless and efficient experience. The structure of these systems typically includes several key components and features:
User Interface (UI):
The User Interface is the faultfinding gateway through which users interact with a system or software, shaping their overall experience.
- Inbox: The central hub where people can access their incoming mails.
- Folders/Labels: Organizational tools for categorizing and managing inbox.
- Search: Robust search functionality for finding specific emails quickly.
- Customize the feature for creating and sending new messages.
Email Storage
Email storage refers to the system and infrastructure used to store and manage related data within a service or client. It is a major aspect of communication ensuring that messages, attachments, and associated information are securely stored and easily retrievable.
- Cloud-Based Storage: Top webmail systems store messages and attachments in the cloud, ensuring accessibility from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Large Storage Capacity: These systems offer generous storage limits that can easily accommodate a substantial volume of mail and attachments.
Security
Security in a webmail system is a major aspect that encompasses various measures and protocols to safeguard user data, privacy, and communications.
- Encryption: Emails are often transmitted and stored with encryption to protect user data.
- Spam and Phishing Filters: Advanced algorithms to filter out unwanted and potentially harmful emails.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a security layer to deter unauthorized access, necessitating individuals to furnish two distinct authentication elements, commonly a knowledge-based factor like a password and a possession-based factor such as a mobile device or security token.
Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility in a webmail system refers to its ability to provide a seamless and user-friendly experience for individuals accessing their accounts from mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets.
- Mobile Apps: These are applications designed specifically for iOS and Android devices, providing a native and optimized experience for users on these platforms.
- Responsive Web Design: A mobile-friendly web interface for accessing on any device.

Productivity Features
Productivity features in webmail systems encompass a range of tools and functionalities designed to enhance users’ efficiency and effectiveness in managing their emails and related tasks. These features aim to streamline communication and help in staying organized.
- Offline Access: Some webmail systems allow netizens to access and compose drafts without an internet connection.
- Synchronization: Real-time synchronization across devices for a consistent experience.
- Undo Send: The option to retract shortly after sending it.
Analytics and Insights
Analytics and insights in a webmail system refer to the tools and functionalities that provide users with valuable data and information about their usage, communication patterns, and the effectiveness of their campaigns.
These features enable someone to make data-driven decisions and enhance their communication strategies.
- Email Tracking: Tools for tracking when emails are opened and read.
- Usage Statistics: Insights into email usage patterns and statistics.
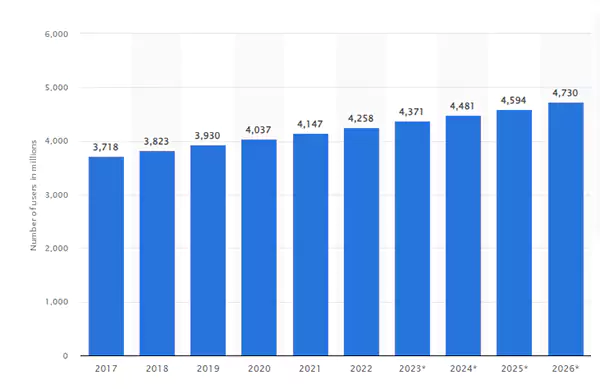
Here, you can see the number of people using emails as communication in current times, as well as estimated future numbers.
Support and Help Resources
Support and help resources in webmail systems are necessary components that provide individuals with assistance, guidance, and solutions to various issues and inquiries they may encounter when using the service. These resources aim to ensure a smooth and user-friendly experience.
- Help Center: A resource for FAQs and troubleshooting.
- Customer Support: Options for contacting customer support for assistance.
Advertisement and Promotion
Advertisement and promotion in webmail systems refer to the inclusion of marketing content and promotional messages within the interface.
Whereas email providers primarily offer free services, they often monetize these services by displaying advertisements to users.
- Ad Integration: Many free webmail systems include ads to monetize the service.
- Promotions Tab: Some webmail systems segregate promotional emails from regular messages, placing them in a separate “Promotions” tab or folder. This feature helps users manage and declutter their primary inbox.
Conclusion
These top-performing webmail systems continuously evolve and improve their features and security measures to meet users’ changing needs and expectations when also addressing emerging cybersecurity threats.
Moreover, they often provide a seamless user experience across multiple devices, making it easy for people to manage email communication from anywhere.